Abstract
Introduction
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a devastating subtype of extranodal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) that accounts for ~4% of newly diagnosed central nervous system (CNS) tumors. (NeuroOncol PMID: 21915121) The age-adjusted incidence of PCNSL in the U.S. has increased since the 1970s. (ACS PMID: 19273630) despite advances in the treatment of lymphoma, and clinical outcomes remain poor with an estimated 5- year survival for immunocompetent patients at 30%. (NCBIPMID:31424729) Trends in outcomes of PCNSL have been reported, but sub-analyses for minorities like Hispanics (HI), have not been widely studied. Understanding ethnic disparities on outcomes and patterns of care in PCNSL are crucial given the rapid growth of HI in the U.S. This study aims to examine the demographics, treatment patterns, and survival outcomes of PCNSL in HI compared to Non-Hispanics (NH) in Texas (TX) and Florida (FL).
Methods
This is a retrospective study of a cohort of patients diagnosed with lymphoma (Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin) from the TX Cancer Registry (TCR) and the FL Cancer Data System (FCDS) from 2006-2017. Patients with PCNSL were identified by the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology Third Edition (ICD-O-3) code list. Standard demographic variables collected include gender, ethnicity, dates at diagnosis and death, primary payer at diagnosis, type of treatment and poverty index (PI). The significance of variation in the distribution of categorical outcomes with ethnicity (HI and NH) was assessed with Fisher's Exact tests or Pearson's Chi-square tests as appropriate; age was assessed with T-tests or Wilcoxon tests as appropriate. Survival distributions were described with Kaplan-Meier curves and significance of variation in median survival with ethnicity was assessed with log rank testing. All statistical testing was two-sided with a significance level of 5%.
Results
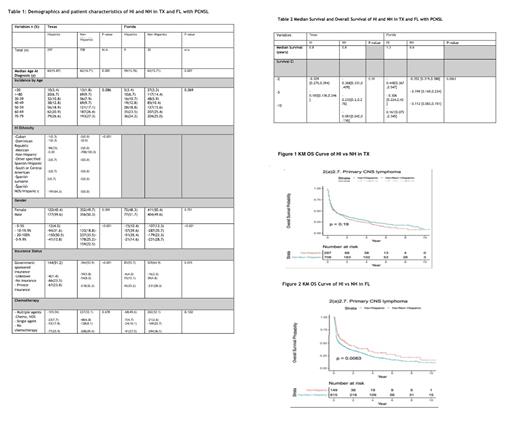
The study included 1969 patients (TX: n=297 HI, n= 708 NH; FL: n=149 HI, n=415 NH). PCNSL was diagnosed at younger median age in HI (TX: 59,FL:59) compared to NH (TX: 62, FL:63),with a significant difference noted within each state (TX: p= 0.005; FL: p=0.007). HI in TX were identified primarily as Mexican, Spanish or NOS/Hispanic. There was a significant predominance of overall males (M) in TX (p=0.009). There was a non-significant predominance of M in FL. Regarding poverty index (PI), there were more HI (TX:51% and FL: 35%) in the 20-100% bracket than NH (TX: 25%; FL: 22%). Conversely there were more NH in all other PI in TX and FL. Government sponsored insurance was the most common insurance in all subgroups. This reached a significant predominance in HI (54%) and NH (54%) in TX (p<0.001). There was no significant difference in insurance types between HI and NH in FL(p=0.772). Regarding chemotherapy there was a trend to either use multiple agents [(TX: 34% in HI vs 32% in NH; p=0.68); (FL: 33% in HI vs 67% in NH; p=0.042)] or to not offer chemotherapy at all [(TX: 26% in HI vs 29% in NH; p= 0.68); (FL: 44% in HI vs 33% in NH; p=0.042)] with significant differences noted in FL only. (Table 1) The median survival (MS) for HI and NH in TX was similar in years (y) at 0.8 while the MS time in FL for HI vs NH was higher (1.3 vs 0.6 respectfully) Thus, the MS for HI in FL was higher compared to NH in FL and HI and NH in both TX and FL. (Table 2) The survival probability for HI was shorter at 2 and 5 years compared to NH in TX with a non-significant overall survival (OS) probability (p-value=0.19) seen in Figure 1. Significantly, the survival probability of HI in FL at 2, 5 and 10 years was higher compared to NH with an OS probability (p-value=0.0063) seen in Figure 2.
Conclusion
This retrospective study showed a statistically significant difference in OS probabilities at all years between HI and NH in FL with PCNSL. The OS probability also remained higher in HI in FL compared to both HI and NH in TX. In addition, the study demonstrated a longer MS in HI in FL compared to not only HI in TX, but also both NH in TX and FL. Sociodemographic differences like gender and insurance types were noted between HI in TX and FL. HI origin groups are also a subject of interest. The primary HI origin group in TX were Mexican and not otherwise specified (NOS). This data was missing for FL HI. Future studies should be conducted to uncover any further disparities between these two HI populations to explore the impact of access to care and disease biology on PCNSL survival outcomes.
Diaz Duque: Incyte: Consultancy; Morphosys: Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Hutchinson Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Epizyme: Consultancy; ADCT: Consultancy.